

Next: Bump Mapping
Up: Implementation
Previous: Register Combiners
Lighting can be computed in an arbitrary 3D coordinate system as long as all
vector parameters involved are oriented with respect to the same coordinate
system [10]. This allows one to select the most convenient
coordinate system for lighting. Tangent space is just such a local
coordinate system. There are two reasons why lighting in tangent space is very
efficient. The first one is that the normal vector 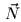 equals always
equals always
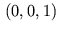 in tangent space, therefore
in tangent space, therefore 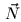 needs no longer interpolated
and normalized. The second reason is that in tangent space the perturbed
normal for bump mapping can be read directly from a texture2 as Kilgard[10]
develop. The orthonormal basis for tangent space is formed by the surface
normal
needs no longer interpolated
and normalized. The second reason is that in tangent space the perturbed
normal for bump mapping can be read directly from a texture2 as Kilgard[10]
develop. The orthonormal basis for tangent space is formed by the surface
normal 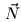 , the surface tangent vector
, the surface tangent vector 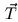 , and the binormal
, and the binormal
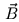 defined as
defined as
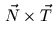 (Figure 6)
(Figure 6)
Figure 6:
Definition of Tangent Space
|
|
For the illumination calculation to proceed properly, the light
and half-angle vectors are transformed into tangent space via a 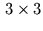 matrix whose columns are
matrix whose columns are 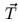 ,
, 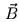 , and
, and 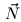 . The
transformations of the light and half-angle vectors should be performed at
every pixel; however, if the change of the local tangent space across a
polygon is small, a good approximation can be obtained by transforming the
vectors only at the polygon vertices. They are then interpolated and
normalized in the polygon interior. Therefore tangent space is constructed
efficiently on a per-vertex basis with the help of a vertex shader
(Section 3.1).
. The
transformations of the light and half-angle vectors should be performed at
every pixel; however, if the change of the local tangent space across a
polygon is small, a good approximation can be obtained by transforming the
vectors only at the polygon vertices. They are then interpolated and
normalized in the polygon interior. Therefore tangent space is constructed
efficiently on a per-vertex basis with the help of a vertex shader
(Section 3.1).


Next: Bump Mapping
Up: Implementation
Previous: Register Combiners
Gerald Schröcker
2002-03-21
![]() equals always
equals always
![]() in tangent space, therefore
in tangent space, therefore ![]() needs no longer interpolated
and normalized. The second reason is that in tangent space the perturbed
normal for bump mapping can be read directly from a texture2 as Kilgard[10]
develop. The orthonormal basis for tangent space is formed by the surface
normal
needs no longer interpolated
and normalized. The second reason is that in tangent space the perturbed
normal for bump mapping can be read directly from a texture2 as Kilgard[10]
develop. The orthonormal basis for tangent space is formed by the surface
normal ![]() , the surface tangent vector
, the surface tangent vector ![]() , and the binormal
, and the binormal
![]() defined as
defined as
![]() (Figure 6)
(Figure 6)